Selecting Cloud GPU Instances
When I need to provision GPU instances for inference, I want to systematically compare options across clouds, so I can select the most cost-effective instance that meets my performance requirements.
The Challenge
You need to provision GPU instances for a new inference deployment. Your requirements: enough memory to run Llama 70B quantized, enough throughput to serve 100 requests/minute, and cost under $10K/month. Simple requirements, but the cloud pricing pages make it anything but simple.
AWS offers p5, p4d, p4de, g5, g6, and g4dn instances—each with different GPU models, counts, and pricing. GCP has a2 and a3 families with different naming conventions. Azure uses yet another scheme. And that’s just NVIDIA GPUs. What about TPUs for training? Trainium for cost-optimized inference? The comparison matrix becomes unmanageable.
This walkthrough shows how to use the Accelerator Registry to navigate cloud GPU options, compare specifications, and select the optimal instance for your workload.
The Starting Point: Your Requirements
You’re the platform lead planning inference infrastructure:
- Model: Llama 70B with AWQ 4-bit quantization (~17.5 GB)
- Serving: vLLM with tensor parallelism
- Throughput: 100 requests/minute
- Latency: P95 < 2 seconds
- Budget: $10K/month maximum
- Cloud: Flexible between AWS, GCP, Azure
Your goal: identify the most cost-effective instance that meets your requirements.
Step 1: Open the Registry
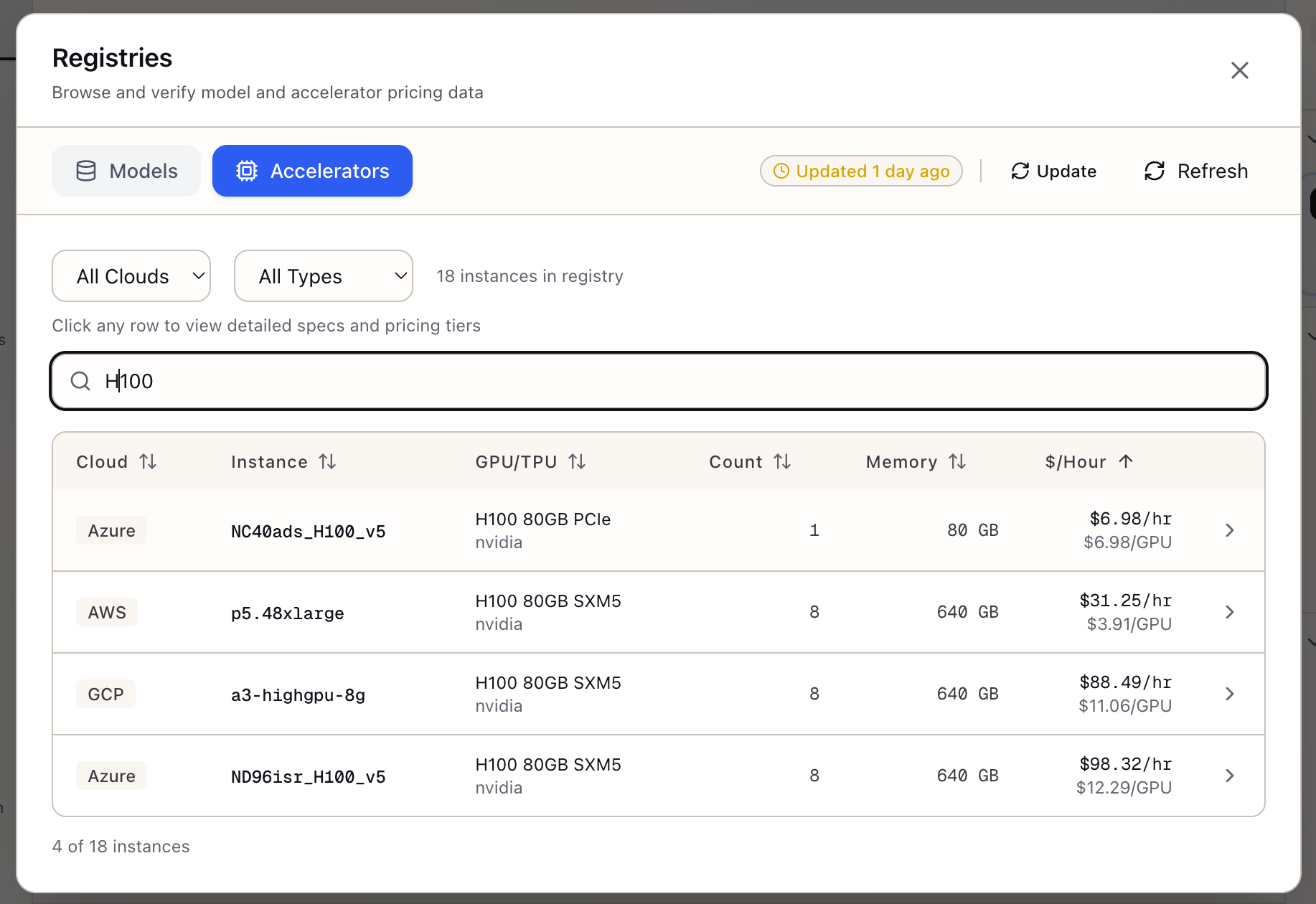
Click the Registries icon in the logo bar of the Sources panel. The Registry Viewer modal opens.

Navigate to Accelerators:
- Click the Accelerators tab in the modal header
- The instance table loads with all cloud GPU/TPU instances
Step 2: Filter by Requirements
Your quantized model is 17.5 GB. With KV cache and overhead, you need ~24 GB per GPU minimum. Filter to relevant instances.
Search for specific accelerators:
- Type “A100” in the search box
- The table filters to A100 instances
- Clear search and try “L4”
Note the per-GPU memory for each type:
- H100 80GB: 80 GB per GPU
- A100 80GB: 80 GB per GPU
- A100 40GB: 40 GB per GPU
- L4: 24 GB per GPU
L4 at 24 GB is tight but workable for your 17.5 GB quantized model.
Step 3: Compare Instance Classes
Let’s compare three instance classes that could work:
Option A: Single L4 (g6.xlarge)
- 1x L4, 24 GB memory, $0.81/hour
- Monthly: $591
Option B: Single A100 40GB (a2-highgpu-1g)
- 1x A100 40GB, 40 GB memory, $3.67/hour
- Monthly: $2,679
Option C: Single A100 80GB (p4de partial)
- Only 8-GPU instances available (~$41/hour)
- Too expensive for single-model inference
Step 4: Validate Throughput Capability
L4 is cheap, but can it hit 100 requests/minute?
Throughput calculation:
100 requests/minute = 1.67 requests/secondAverage output: 300 tokensRequired throughput: 1.67 x 300 = 500 tokens/second
Single L4 capacity: ~20 tokens/secondGPUs needed: 500 / 20 = 25 L4 GPUsA single L4 won’t meet throughput. Let’s check A100.
Step 5: Analyze A100 Instance
A100 Inference Performance:
- ~50-60 tokens/second for 70B quantized
- 500 / 55 = ~9 A100 GPUs needed
Pricing (a2-highgpu-1g on GCP):
| Tier | Hourly | Monthly (730h) |
|---|---|---|
| On-Demand | $3.67 | $2,679 |
| Spot | $1.10 | $803 |
9x A100 monthly cost:
- On-Demand: 9 x $2,679 = $24,111 (over budget)
- Spot: 9 x $803 = $7,227 (under budget!)
Step 6: Finalize the Configuration
Recommended Configuration:
Instance: a2-highgpu-1g (GCP)Count: 9 instancesGPU: 9x A100 40GB (independent)Pricing: SpotMonthly Cost: $7,227
Throughput: ~500 tokens/second (9 x 55)Latency: ~300ms (single request)Alternatives considered:
| Option | Instances | GPUs | Monthly Cost | Fits Budget |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L4 spot | 25 | 25x L4 | $5,850 | Yes but complex |
| A100 spot | 9 | 9x A100 40GB | $7,227 | Yes |
| A100 8-GPU spot | 3 | 24x A100 40GB | $19,314 | No |
Step 7: Export and Document
Save as Artifact: Click Save as Artifact in the detail panel to capture your analysis with configuration, rationale, and trade-offs documented.
Real-World Patterns
Pattern: Balancing Latency and Cost
If P95 latency is critical:
- Filter for H100 (3x faster than A100)
- Accept higher hourly cost for fewer instances
- Consider TP across multi-GPU instances for single-request speedup
Pattern: Training vs Inference Instances
For training workloads:
- Prioritize memory bandwidth (A100/H100 HBM)
- Consider interconnect for multi-GPU (NVLink > PCIe)
- Look at total memory for large batch sizes
For inference:
- Prioritize INT8/FP16 TOPS over memory bandwidth
- L4 often best cost/performance for smaller models
- A10G is middle ground between L4 and A100
Pattern: Cross-Cloud Arbitrage
Same GPU, different prices:
- Sort by hourly rate to find cheapest option
- Check spot availability across regions
- GCP often cheaper for A100
- AWS often cheaper for H100
What You’ve Accomplished
You now have a systematic approach to GPU selection:
- Filtered instances by memory requirements
- Compared throughput capability against requirements
- Calculated monthly costs with different pricing tiers
- Identified optimal configuration within budget
What’s Next
Your instance selection flows into other Lattice tools:
- Memory Calculator: Verify model fits with detailed memory breakdown
- Spot Instance Advisor: Configure spot strategy for selected instances
- TCO Calculator: Include selected instance in total cost analysis
- Stack Configuration: Apply instance type to infrastructure stack
Accelerator Registry is available in Lattice. Make hardware decisions with current, comparable data.
Ready to Try Lattice?
Get lifetime access to Lattice for confident AI infrastructure decisions.
Get Lattice for $99