Configuring Stack Hardware Settings
When I need to specify infrastructure for my AI workload, I want to configure hardware settings for my stack, so I can control cloud provider, GPU type, and compute resources.
Introduction
In Lattice, the Hardware section of a stack defines where and how your AI workload runs. This includes cloud provider selection (AWS, GCP, Azure), GPU type for inference or training (H100, A100, T4), instance configuration, and region selection.
Hardware configuration directly impacts cost, latency, and performance. The right configuration depends on your workload requirements, budget constraints, and geographic needs.
Step 1: Access Stack Configuration

The ContextBar displays your current stack:
Quick Access
- Stack Name: Shows which stack you’re using
- Edit Button: Pencil icon opens configuration
- Scenario Context: Your workload requirements
Click the edit button to open the StackConfigForm and navigate to hardware settings.
Step 2: Stack Configuration Form
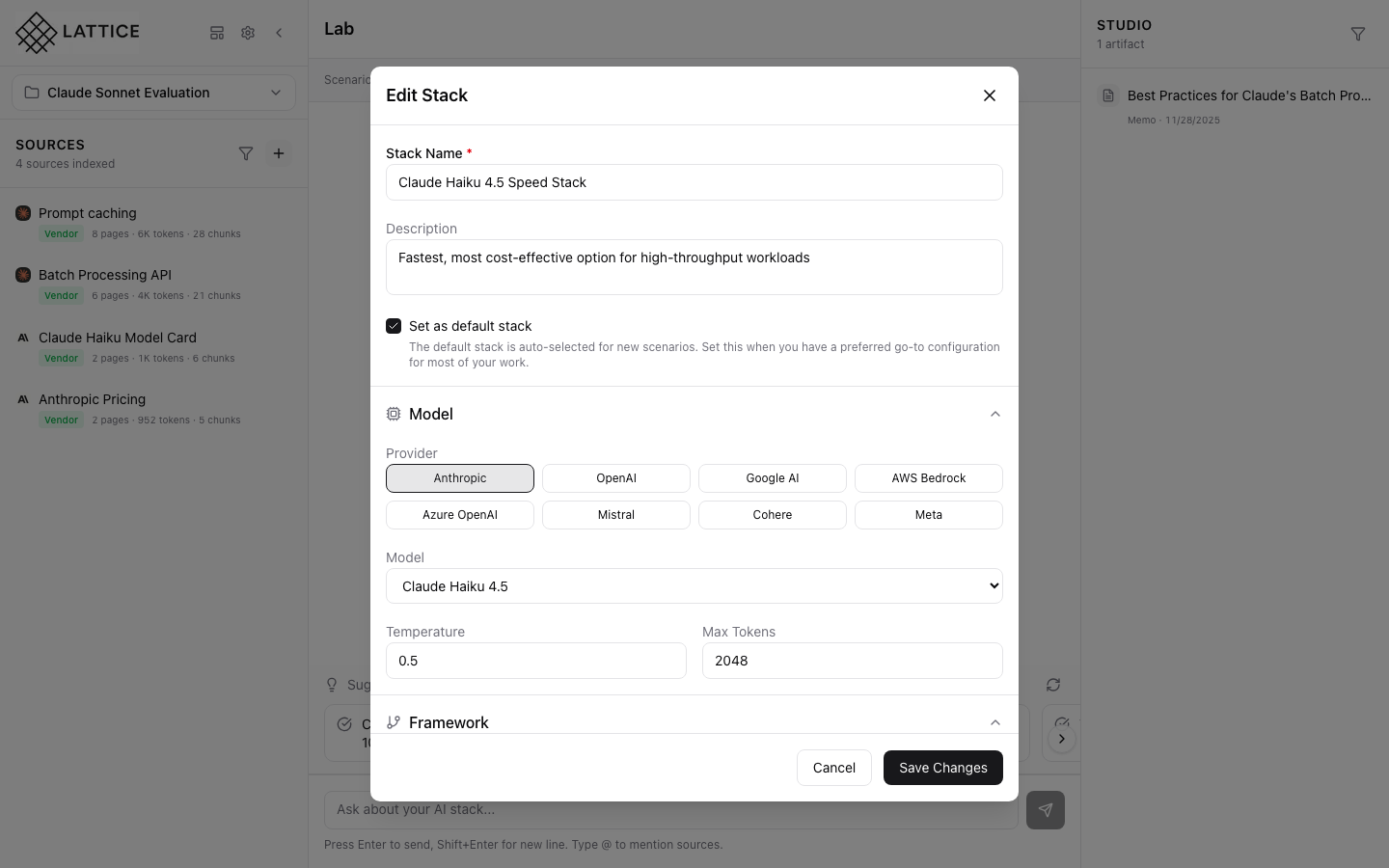
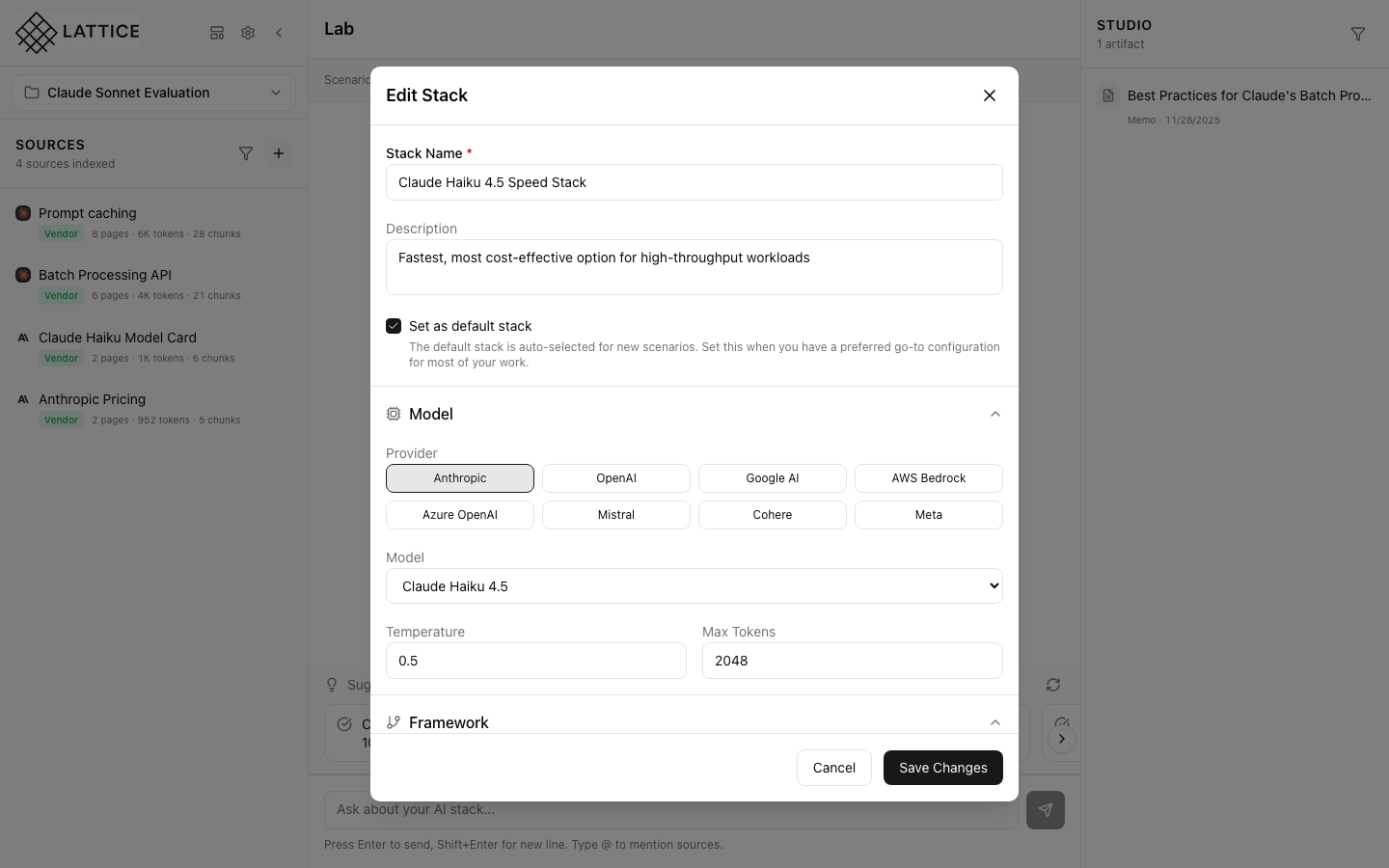
The StackConfigForm opens with sections for complete configuration:
Available Sections
- Model: AI provider and model settings
- Framework: Orchestration and observability
- Hardware: Cloud and compute configuration (scroll to access)
Scroll down past the Framework section to reach Hardware settings.
Step 3: Cloud Provider and Instance
The Hardware section shows cloud configuration:
Cloud Provider
- AWS: Amazon Web Services
- GCP: Google Cloud Platform
- Azure: Microsoft Azure
Instance Configuration
- Instance Family: GPU-optimized, compute-optimized, memory-optimized
- Instance Size: Small, medium, large, xlarge
- Spot Instances: Cost-saving option with interruption risk
Provider selection affects available instance types, pricing, and regional availability.
Step 4: GPU and Region Configuration
Scrolling further reveals GPU and region settings:
GPU Type
- H100: Latest generation, highest performance
- A100: High performance, widely available
- A10G: Balanced performance and cost
- T4: Cost-effective for inference
Region Selection
- Primary Region: Main deployment location
- Latency Optimization: Choose regions close to users
- Data Residency: Meet compliance requirements
Advanced Options
- Multi-GPU: Configure multiple GPUs per instance
- Reserved Capacity: Guaranteed availability
- Spot Fallback: Automatic fallback from spot to on-demand
What You’ve Accomplished
You’ve learned how to configure hardware settings in Lattice:
- Access configuration — Click edit button on current stack
- Navigate to Hardware — Scroll past Model and Framework sections
- Select cloud provider — Choose AWS, GCP, or Azure
- Configure instances — Set family, size, and spot options
- Choose GPU — Select appropriate GPU for your workload
- Set region — Pick deployment region
Key benefits of hardware configuration:
- Cost control — Choose cost-effective options for your budget
- Performance optimization — Select GPUs matching your latency needs
- Geographic placement — Deploy close to your users
- Compliance — Meet data residency requirements
Next steps: Compare GPU options for your latency requirements, or evaluate spot instance savings for non-critical workloads.
Ready to Try Lattice?
Get lifetime access to Lattice for confident AI infrastructure decisions.
Get Lattice for $99